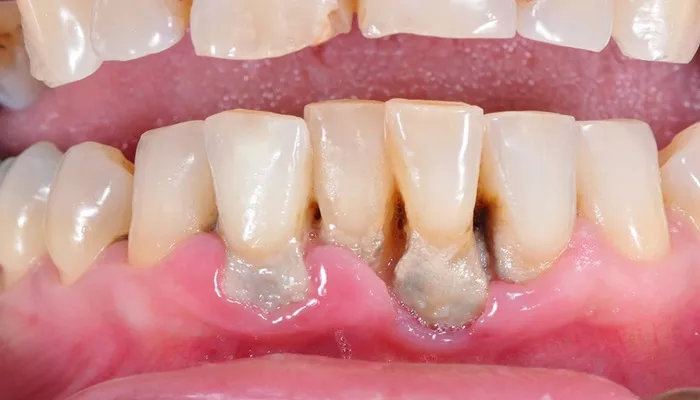
Periodontal disease, commonly referred to as gum disease, is a significant oral health issue affecting millions of individuals worldwide. It encompasses a range of inflammatory conditions that affect the tissues surrounding the teeth. The disease begins with gingivitis, characterized by inflammation and irritation of the gingiva (gums), and can progress to periodontitis, which involves the destruction of the supporting structures of the teeth, including bone. If left untreated, periodontal disease can lead to tooth mobility and loss. Understanding the causes of periodontal disease is crucial for prevention and effective management. This article delves into the various factors contributing to the development of periodontal disease, highlighting both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors.
What Is Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease is an infection that affects the gums and other structures supporting the teeth. It can be classified into two main categories:
Gingivitis: This is the earliest stage of periodontal disease, marked by gum inflammation without loss of bone or tissue.
Periodontitis: This advanced stage involves deeper infections that can lead to significant damage to the bone and connective tissue that support teeth.
The progression from gingivitis to periodontitis occurs when plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—accumulates on teeth and hardens into tartar. If not removed through proper oral hygiene, this buildup can lead to inflammation and infection.
Causes of Periodontal Disease
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
One of the primary causes of periodontal disease is inadequate oral hygiene. When individuals fail to brush and floss regularly, plaque accumulates on their teeth. Over time, this plaque hardens into tartar, which cannot be removed by brushing alone. The presence of tartar creates an environment conducive to bacterial growth, leading to inflammation and infection in the gums. Regular dental cleanings are essential for removing tartar and preventing gum disease.
2. Tobacco Use
Smoking and other forms of tobacco use are significant risk factors for periodontal disease. Tobacco products impair blood flow to the gums, which affects healing and makes it easier for infections to take hold.
Studies indicate that nearly 70% of patients with periodontal disease are smokers. Quitting smoking can significantly improve gum health and reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease.
3. Genetic Factors
Genetics play a crucial role in an individual’s susceptibility to periodontal disease. Some people may inherit a predisposition to gum disease due to genetic variations that affect immune response or inflammatory processes.
Understanding one’s family history regarding oral health can help identify those at higher risk for developing periodontal issues.
4. Nutritional Deficiencies
A diet lacking essential nutrients can contribute to periodontal disease. Specifically, deficiencies in vitamins such as vitamin C have been linked to gum health; vitamin C is vital for collagen synthesis in gum tissue. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals is essential for maintaining healthy gums and preventing infection.
5. Systemic Health Conditions
Several systemic health conditions can increase the risk of developing periodontal disease:
Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more susceptible to infections due to impaired immune function. High blood sugar levels can also exacerbate gum inflammation.
Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus can compromise immune responses, making it easier for periodontal infections to develop.
Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to infection.
6. Medications
Certain medications can contribute to dry mouth or alter gum tissue, increasing the risk of periodontal disease. For example, medications that reduce saliva flow create an environment where bacteria thrive.
Patients taking such medications should discuss their oral health with their healthcare provider.
7. Stress
Psychological stress can negatively impact oral health by affecting immune function and promoting behaviors such as poor oral hygiene or tobacco use. Stress management techniques may help mitigate these risks.
8. Clenching or Grinding Teeth (Bruxism)
Bruxism, or teeth grinding, places excessive force on the supporting tissues of teeth, potentially leading to gum recession and increased susceptibility to periodontal disease. Individuals who grind their teeth should consult a dentist for management strategies.
9. Age
Advancing age is associated with an increased risk of periodontal disease due to cumulative exposure to risk factors over time. Older adults may also have a higher prevalence of systemic diseases that contribute to gum health decline.
10. Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic status influences access to dental care and education about proper oral hygiene practices. Individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may face barriers that prevent them from receiving adequate dental care, increasing their risk for periodontal diseases.
The Role of Bacteria in Periodontal Disease
The primary instigator of periodontal disease is bacterial plaque—a biofilm composed of numerous bacterial species that adhere to tooth surfaces. When plaque is not adequately removed through brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, further promoting bacterial growth below the gum line. The bacteria release toxins that irritate the gums and trigger an immune response characterized by inflammation.
As the body attempts to fight off this bacterial invasion, it may inadvertently cause damage to its own tissues. This process leads to the formation of pockets between the gums and teeth where additional bacteria can thrive, exacerbating tissue destruction over time.
Conclusion
Periodontal disease is a complex condition influenced by various factors ranging from personal habits like oral hygiene practices to systemic health issues like diabetes. By understanding these causes and implementing preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing this prevalent condition. Regular dental care combined with healthy lifestyle choices plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal gum health and preventing tooth loss associated with periodontal disease.