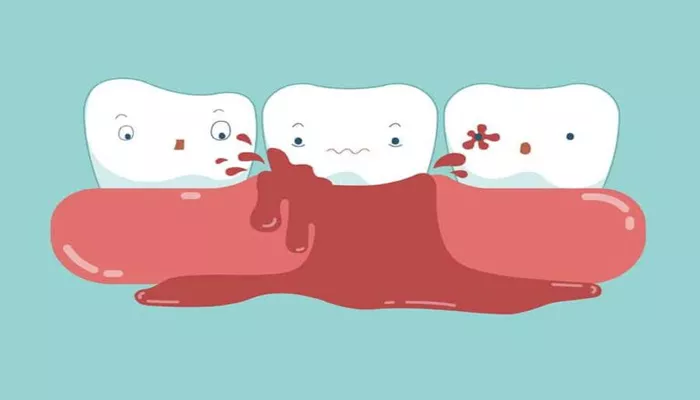
Early periodontal disease, often referred to as early periodontitis, is a condition where the gums and bone supporting the teeth become inflamed. This inflammation is typically caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth, leading to symptoms such as red, swollen, or bleeding gums. If left untreated, early periodontitis can progress to more severe stages, potentially resulting in tooth loss and other serious oral health issues. However, with early detection and appropriate treatment, it is possible to manage and even reverse the condition.
Understanding Periodontal Disease Stages
Periodontal disease progresses through several stages, starting from gingivitis, which is the earliest and most reversible form. Gingivitis is characterized by inflammation of the gums without any loss of bone or tissue. As the disease progresses, it can lead to periodontitis, where the bone and tissue supporting the teeth begin to deteriorate. Early periodontitis is a critical stage where intervention can significantly impact the outcome.
Causes of Early Periodontal Disease
Early periodontal disease is primarily caused by poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to accumulate on the teeth. Other factors can contribute to the development of periodontal disease, including:
Genetics: Some people are more prone to gum disease due to genetic predisposition.
Smoking: Tobacco use significantly increases the risk of developing periodontal disease.
Diabetes: People with diabetes are more susceptible to infections, including gum disease.
Poor Diet: A diet lacking essential nutrients can weaken the body’s ability to fight off infections.
Symptoms of Early Periodontal Disease
Identifying the symptoms of early periodontal disease is crucial for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing.
Swollen or Red Gums: Gums that appear red, swollen, or tender.
Bad Breath: Persistent bad breath that does not improve with regular brushing.
Loose Teeth: Teeth that feel loose or shift when touched.
Treatment Options for Early Periodontal Disease
Treating early periodontal disease involves a combination of professional dental care and lifestyle changes. The goal is to remove plaque and bacteria, reduce inflammation, and prevent further progression of the disease.
Professional Dental Treatments
Scaling and Root Planing: This is a non-surgical procedure that involves deep cleaning of the teeth and roots to remove plaque and tartar. It helps smooth the root surfaces, allowing the gums to heal and reattach to the teeth.
Antibiotics: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infections. These can be taken orally or applied directly to the affected areas.
Regular Dental Cleanings: Regular cleanings are essential for maintaining oral health and preventing the buildup of plaque and tartar.
Lifestyle Changes
Improved Oral Hygiene Practices: Brushing teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can help control plaque buildup.
Dietary Adjustments: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps support overall oral health.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is crucial for reducing the risk of periodontal disease progression.
Regular Dental Visits: Regular check-ups with a dentist are vital for early detection and treatment of gum disease.
Surgical Options for Advanced Cases
While early periodontal disease can often be managed with non-surgical treatments, more advanced cases may require surgical intervention.
Pocket Reduction Surgery: This involves making an incision in the gum to access and clean deep pockets around the teeth.
It helps reduce the depth of these pockets, making it easier to maintain oral hygiene.
Bone Grafting: If bone loss has occurred, bone grafting may be necessary to restore the supporting structures around the teeth.
LANAP (Laser-Assisted New Attachment Procedure): This is a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery, using a laser to target diseased tissue while preserving healthy tissue.
Preventing Periodontal Disease
Prevention is key in managing periodontal disease. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene practices can significantly reduce the risk of developing gum disease.
Regular Brushing and Flossing: Daily brushing and flossing help remove plaque and prevent tartar buildup.
Dental Visits: Regular dental cleanings and exams are essential for detecting early signs of gum disease.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding tobacco products can reduce the risk of periodontal disease.
Conclusion
Early periodontal disease is a treatable condition that, with prompt intervention, can be managed effectively. By combining professional dental treatments with lifestyle changes, individuals can prevent the progression of the disease and maintain good oral health. It is crucial to recognize the symptoms early and seek professional advice to ensure the best possible outcomes.