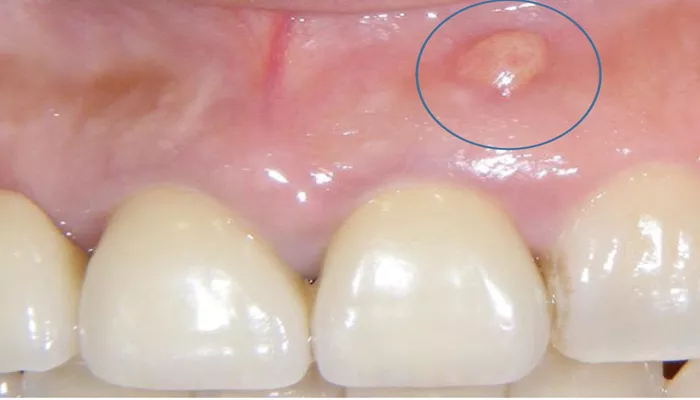
An abscess on the gum is a painful condition that occurs when a pocket of pus forms in the tissue surrounding a tooth. This infection can lead to severe pain, swelling, and discomfort, and if left untreated, it can cause serious complications. In this article, we will discuss what a gum abscess is, its causes, symptoms, and the various ways to treat it.
What Is A Gum Abscess?
A gum abscess, also known as a periodontal abscess, is an infection that typically forms at the base of a tooth or around the gum tissue. It happens when bacteria invade the gum tissues, leading to inflammation and the formation of pus. The infection may start small but can rapidly become more severe without treatment.
Abscesses can also occur in other parts of the mouth, such as the roots of the teeth (periapical abscess), but gum abscesses specifically affect the soft tissues around the teeth. These abscesses often cause discomfort, redness, swelling, and, in some cases, fever.
Causes of Gum Abscess
Several factors contribute to the formation of a gum abscess:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which may result in gum infections.
Tooth Decay: Cavities that are left untreated can create entry points for bacteria, leading to gum abscesses.
Gum Disease (Periodontitis): Long-standing gum disease can cause pockets in the gums, trapping bacteria and leading to abscess formation.
Trauma: Injuries to the mouth, such as cuts or a fractured tooth, can create openings for infections to develop.
Dental Procedures: Sometimes, dental procedures such as root canals or extractions can lead to bacterial infections if proper aftercare is not followed.
Symptoms of A Gum Abscess
The symptoms of a gum abscess can vary depending on its severity but typically include:
Pain or Tenderness: Pain that increases when chewing or touching the affected area.
Swelling: Swollen and red gums around the affected tooth.
Pus Drainage: Pus may drain from the abscess, which can provide temporary relief from the pain.
Bad Breath (Halitosis): A foul odor from the mouth due to the bacterial infection.
Fever: In severe cases, a fever may develop as a response to the infection.
Sensitivity: Increased sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages.
Treatment Methods for Gum Abscess
1. Professional Dental Care
The most effective way to treat a gum abscess is to seek care from a dental professional. Dentists can perform specific procedures to relieve pain, remove infection, and prevent future abscesses. Here are the steps involved in professional care:
Drainage of the Abscess
If the abscess is large, the dentist may need to drain the pus to relieve pressure and pain. They will make a small incision in the abscess to allow the pus to drain out. This procedure is typically done under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
Deep Cleaning (Scaling and Root Planing)
In cases where gum disease is the underlying cause, a deep cleaning may be required. This procedure involves scaling, which removes plaque and tartar from the surfaces of the teeth, followed by root planing to smooth out rough areas of the tooth roots. This helps to remove bacteria from the deeper pockets in the gums.
Antibiotics
To treat the infection, a dentist may prescribe antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the abscess. These medications may be taken orally or applied directly to the infected area, depending on the severity of the infection.
Tooth Extraction
In some cases, the infection may have damaged the tooth beyond repair. If this happens, the dentist may recommend extracting the affected tooth to prevent the infection from spreading.
Root Canal Treatment
If the abscess is caused by an infection in the tooth’s root, a root canal may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the infected tissue from inside the tooth, disinfecting it, and then sealing it to prevent further infections.
2. Home Remedies for Gum Abscess
While professional care is essential for treating a gum abscess, some home remedies can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling in the meantime. These remedies do not replace professional treatment but can provide temporary relief.
Salt Water Rinse
A salt water rinse is one of the simplest and most effective ways to reduce swelling and clean the affected area. Mix one teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth several times a day.
This helps to promote healing and reduce bacterial growth.
Cold Compress
Applying a cold compress to the outside of your cheek near the infected area can help reduce swelling and numb the pain.
Use a cold pack wrapped in a cloth and hold it against your cheek for 15 to 20 minutes.
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help relieve pain and inflammation associated with a gum abscess. However, these should only be used temporarily, and they do not address the root cause of the infection.
Hydrogen Peroxide Rinse
A hydrogen peroxide rinse can help disinfect the area and reduce bacteria in the mouth. Mix equal parts of hydrogen peroxide (3%) and water, then swish it around your mouth for 30 seconds. Be sure not to swallow the solution.
3. Preventing Future Gum Abscesses
Once a gum abscess is treated, it’s important to take steps to prevent future occurrences. Some preventive measures include:
Proper Oral Hygiene
Brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce plaque buildup and prevent infections.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Visiting the dentist regularly (every 6 months) allows them to detect early signs of gum disease, cavities, or other oral health issues before they develop into more serious conditions like abscesses.
Dietary Choices
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports gum health. Avoid sugary foods and drinks that can contribute to plaque buildup and tooth decay.
Avoid Smoking
Smoking impairs the body’s ability to heal and increases the risk of gum disease, making it easier for abscesses to form.
Quitting smoking can improve your overall oral health.
4. When to Seek Emergency Dental Care
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek immediate dental care:
Severe, Uncontrollable Pain: If the pain becomes unbearable or spreads to other parts of the mouth, face, or neck, it may indicate that the infection is spreading.
Swelling That Interferes with Breathing or Swallowing: If the swelling is causing difficulty breathing or swallowing, this is a medical emergency, and immediate treatment is required.
Fever: A high fever alongside an abscess can signal a severe infection that requires urgent attention.
Conclusion
A gum abscess is a serious condition that requires prompt attention. While home remedies may offer temporary relief, professional treatment is essential to fully address the infection and prevent further complications. By following proper oral hygiene practices and seeking dental care, you can reduce your risk of developing gum abscesses and maintain better overall oral health.