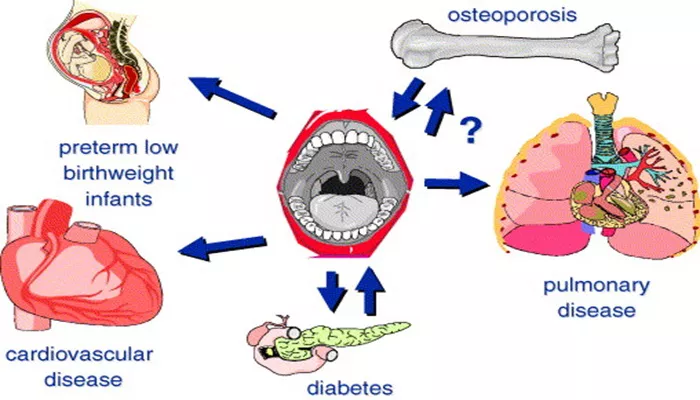
Periodontal disease, often referred to as gum disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that primarily affects the gums and structures supporting the teeth. While it may seem like a localized problem, the impact of periodontal disease extends beyond the mouth, potentially affecting several critical organs and systems throughout the body. This article will explore the connection between periodontal disease and various organs, explaining how it influences overall health.
Introduction
Periodontal disease is a widespread condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It ranges from simple gingivitis, where the gums become inflamed, to more severe periodontitis, which involves damage to the bone and tissues around the teeth. Although many individuals may not experience severe symptoms, untreated periodontal disease can lead to serious complications, some of which may affect organs beyond the mouth. The bacteria that cause periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, influencing various organs and systems. Understanding the organs affected by periodontal disease is crucial for recognizing its potential to cause long-term health problems.
Heart
The Link Between Periodontal Disease and Heart Disease
One of the most well-documented relationships is between periodontal disease and heart disease. Research suggests that the bacteria associated with gum disease can enter the bloodstream through inflamed gum tissue. These bacteria can travel to the heart and potentially contribute to the development of cardiovascular conditions, including heart disease and stroke.
How Periodontal Disease Affects the Heart
The bacteria from periodontal disease may trigger inflammation throughout the body, which is a known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Specifically, the bacteria can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries (atherosclerosis), narrowing the blood vessels and increasing the risk of heart attacks or strokes. Studies have also shown that people with periodontal disease are at higher risk of developing endocarditis, an infection of the heart’s inner lining.
Lungs
Periodontal Disease and Respiratory Health
The connection between periodontal disease and lung health is another area of concern. Inhalation of bacteria from infected gums may cause or worsen respiratory diseases. People with periodontal disease are at a higher risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), pneumonia, and other respiratory infections.
Impact on the Lungs
The bacteria from gum disease can enter the respiratory tract, leading to lung infections and inflammation. Additionally, chronic inflammation in the mouth may contribute to conditions like bronchitis and emphysema. For individuals already suffering from respiratory diseases, untreated periodontal disease can exacerbate symptoms and lead to more severe complications.
Diabetes
Periodontal Disease and Diabetes: A Two-Way Relationship
The relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease is bidirectional. Not only does diabetes increase the risk of developing gum disease, but periodontal disease can also make it harder to control blood sugar levels, complicating diabetes management.
How Periodontal Disease Affects Diabetes
Inflammation caused by gum disease can impair the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to higher blood sugar levels. In people with diabetes, this can cause a vicious cycle, as high blood sugar levels can, in turn, worsen periodontal disease. Managing periodontal disease is crucial for people with diabetes to prevent further complications, such as diabetic complications in the kidneys, eyes, and nerves.
Kidneys
Impact of Periodontal Disease on Kidney Function
Recent research has revealed a connection between periodontal disease and kidney health. Periodontal disease can worsen kidney disease, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions.
How Periodontal Disease Affects the Kidneys
The bacteria from gum disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to the kidneys, leading to increased inflammation. This inflammation can accelerate kidney damage in people with chronic kidney disease, making it more difficult for the kidneys to filter waste from the blood. In severe cases, periodontal disease may contribute to kidney failure, especially in people with other risk factors.
Pregnancy
The Effect of Periodontal Disease on Pregnancy
Pregnancy can influence periodontal health, but the reverse is also true. Periodontal disease can impact pregnancy outcomes, including increasing the risk of premature birth and low birth weight. The inflammatory processes triggered by gum disease may affect fetal development, potentially leading to complications.
How Periodontal Disease Affects Pregnancy
The bacteria from periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream and trigger an inflammatory response in the body. During pregnancy, this inflammation may affect the placenta and lead to complications such as preterm labor and low birth weight.
Additionally, some studies suggest a possible link between periodontal disease and gestational diabetes, which further increases the risks during pregnancy.
Brain
Periodontal Disease and Cognitive Function
Emerging research suggests a connection between periodontal disease and brain health, particularly in relation to cognitive decline and conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease. Chronic inflammation caused by gum disease may play a role in the development of neurodegenerative diseases.
How Periodontal Disease Affects the Brain
The bacteria responsible for periodontal disease may travel to the brain via the bloodstream or the nerves in the mouth, causing inflammation in the brain. Studies have shown that chronic inflammation is associated with cognitive decline and may increase the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and dementia. The presence of specific bacteria from gum disease in the brain may accelerate the development of these conditions, leading to impaired cognitive function.
Digestive System
Periodontal Disease and the Gut
The digestive system can also be impacted by periodontal disease.
The bacteria that cause gum infections can enter the gut and affect the balance of gut bacteria, contributing to digestive problems such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
How Periodontal Disease Affects the Digestive System
The mouth serves as the entry point for food and bacteria into the digestive tract. When the bacteria from periodontal disease enter the gastrointestinal system, they can disrupt the natural balance of gut bacteria, leading to inflammation in the digestive tract. This disruption may exacerbate conditions like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or IBS, making it more difficult to manage these chronic gastrointestinal diseases.
Conclusion
Periodontal disease is not just a problem for the gums and teeth—it can have a far-reaching impact on overall health. From the heart and lungs to the kidneys, brain, and digestive system, untreated gum disease can lead to a variety of serious health conditions. The connection between oral health and systemic health highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking treatment for periodontal disease as early as possible. By addressing gum disease, you can significantly reduce the risk of complications affecting other vital organs and improve your overall well-being.