Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common oral health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It begins with inflammation of the gums (gingivitis) and, if left untreated, can progress to advanced stages, leading to irreversible damage to the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bones. One of the most frequent questions patients have when diagnosed with periodontal disease is whether advanced periodontal disease is reversible.
In this article, we will explore what advanced periodontal disease is, its symptoms, stages, and treatment options. We will also address whether this advanced stage of periodontal disease can be reversed or managed effectively.
What Is Advanced Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease occurs when bacteria in plaque accumulate on the teeth and gums, leading to inflammation and infection. The disease can be categorized into two main stages:
Gingivitis – This is the earliest stage, marked by swollen, red, and bleeding gums. At this point, the condition is usually reversible with proper dental care.
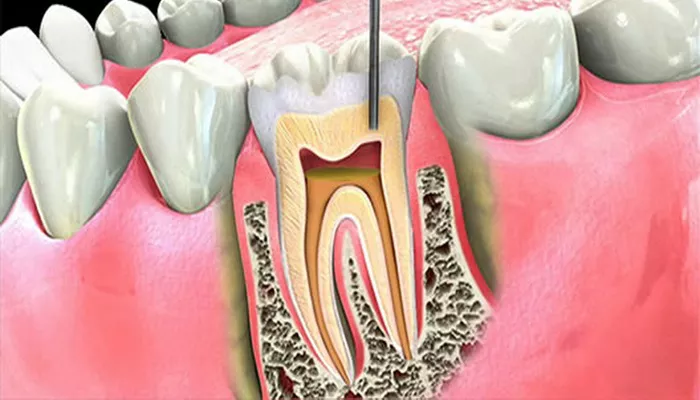
Periodontitis – When gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where the inflammation affects the deeper layers of the gums and supporting bone structure. Periodontitis can be classified into mild, moderate, and advanced stages, with the most severe form being advanced periodontal disease.
In advanced periodontal disease, the infection has caused significant damage to the tissues and bone that support the teeth.
The gums may pull away from the teeth, leading to deep pockets where bacteria can thrive. This stage may result in loose teeth or even tooth loss if not properly managed.
Can Advanced Periodontal Disease Be Reversed?
The straightforward answer is that advanced periodontal disease cannot be fully reversed. At this stage, the damage to the bone and connective tissues is typically irreversible. However, the disease can be managed and the progression halted with appropriate treatment. With the right interventions, it is possible to restore some of the lost function and even improve the overall condition of the gums and supporting structures.
Why Is Advanced Periodontal Disease Not Fully Reversible?
The reason advanced periodontal disease cannot be fully reversed is primarily due to the irreversible damage it causes to the bone and soft tissue structures. Once the bone supporting the teeth is lost, it cannot regrow on its own. Although certain treatments can help regenerate some tissue, such as with bone grafts or soft tissue grafts, the natural healing process is limited in terms of complete restoration.
However, the progression of the disease can be stopped. Treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and minimize further damage to the gums and bone. The goal of treatment at this stage is to restore oral health as much as possible, preserve the teeth, and improve overall comfort.
Symptoms of Advanced Periodontal Disease
Advanced periodontal disease is often marked by several noticeable symptoms that require immediate attention. These include:
Gum recession – Gums begin to pull away from the teeth, exposing more of the tooth or even its roots.
Deep pockets between the gums and teeth – The space between the gums and teeth increases, providing a breeding ground for harmful bacteria.
Loose teeth – As the bone and connective tissue deteriorate, teeth may become loose or shift.
Persistent bad breath – The ongoing infection can lead to a foul-smelling odor in the mouth.
Gum bleeding and pus – The gums may bleed, particularly when brushing or flossing, and pus may be present around the teeth and gums.
Pain while chewing – The discomfort from gum infection and shifting teeth may cause pain when eating.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek professional dental care promptly. Early intervention is key to managing advanced periodontal disease and preventing further damage.
How Is Advanced Periodontal Disease Treated?
The treatment for advanced periodontal disease varies depending on the extent of the condition, but it typically involves a combination of professional dental procedures, home care, and sometimes surgical intervention. Below are the primary treatment options:
1. Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure used to treat moderate to severe periodontal disease. It involves the removal of plaque and tartar (calculus) from the surfaces of the teeth and the roots. This treatment aims to remove bacteria that contribute to the infection and smooth the tooth roots to help the gums reattach to the teeth.
Although this procedure is very effective for managing periodontitis, it is often not enough for advanced stages on its own.
2. Antibiotic Therapy
In cases of advanced periodontal disease, dentists may prescribe antibiotics to help control the infection. These can be topical antibiotics
placed directly on the gums or oral antibiotics to be taken by mouth. Antibiotics help kill the bacteria causing the infection and reduce inflammation.
3. Surgical Treatment
For more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to access the infected tissues beneath the gums. The types of surgical treatments include:
Flap surgery – The gums are lifted to remove tartar and bacteria that may be deeper beneath the gum line. After the cleaning, the gums are repositioned to fit more snugly around the teeth.
Bone grafts – In cases where bone has been lost due to the disease, bone grafts may be used to stimulate bone growth and help preserve the structure of the teeth.
Soft tissue grafts – When the gum tissue has receded significantly, soft tissue grafts can be used to cover the exposed roots, reduce sensitivity, and restore the appearance of the gums.
Guided tissue regeneration – This procedure involves placing a special membrane between the gum and bone to encourage the growth of new bone and tissue.
4. Regular Maintenance Care
Even after treatment, patients with advanced periodontal disease need ongoing maintenance care to prevent the disease from returning. This may involve more frequent cleanings, continued use of antibiotics, and improved oral hygiene practices at home.
Managing Advanced Periodontal Disease: Prevention And Maintenance
While advanced periodontal disease cannot be reversed, there are several key strategies that can help prevent further progression and maintain oral health:
1. Good Oral Hygiene
Proper brushing and flossing are essential for managing periodontal disease. Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily helps remove plaque and food particles that contribute to bacterial growth.
2. Regular Dental Checkups
Routine dental visits are crucial for monitoring the condition of your gums and teeth. Professional cleanings, performed every 3-6 months, are necessary to remove plaque and tartar buildup that cannot be eliminated with regular brushing.
3. Healthy Diet
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals helps maintain gum health. Foods high in vitamin C, calcium, and antioxidants can help support the healing process and strengthen the immune system, making it easier for your body to fight off infection.
4. Avoid Tobacco Use
Smoking and using other forms of tobacco significantly increase the risk of developing periodontal disease and hinder the healing process. Quitting smoking can improve the outcome of periodontal treatment and prevent further complications.
5. Managing Systemic Health Issues
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, can worsen periodontal disease. Keeping these conditions under control can help improve your oral health and prevent the progression of gum disease.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while advanced periodontal disease is not reversible, it can be managed effectively with the right treatments and preventive measures. Early diagnosis, professional dental care, and diligent home care are essential in halting the progression of the disease and improving the health of the gums and teeth.