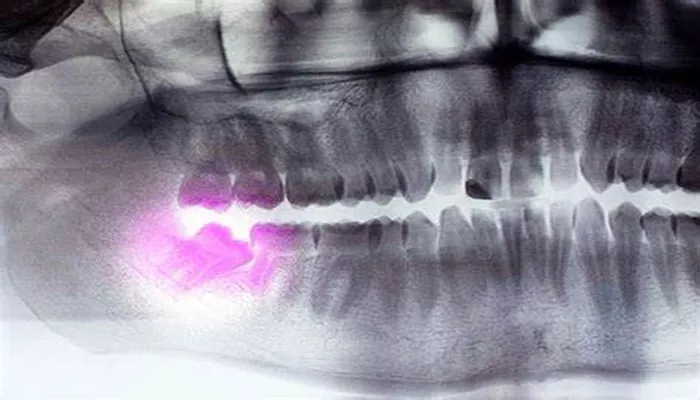
Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of teeth located at the back of your mouth. These teeth typically emerge during late adolescence or early adulthood, often between the ages of 17 and 25. While some people have no issues with their wisdom teeth, others experience discomfort and complications. It is important to understand the signs that your wisdom teeth are coming in, as this can help you determine when to seek professional dental advice.
In this article, we will discuss the common signs that indicate your wisdom teeth are emerging, what you can do to manage any discomfort, and when you should consult with your dentist.
1. Pain or Tenderness at The Back of Your Mouth
One of the first signs that your wisdom teeth are coming in is pain or tenderness at the back of your mouth. This can happen when the teeth begin to push through the gums. The pain may be mild at first, but it can gradually increase as the teeth continue to emerge.
Why Does This Happen?
The pain occurs because the new teeth are forcing their way through the gum tissue, which can be sensitive. The pressure from the teeth as they emerge can also irritate surrounding areas, causing discomfort.
How to Manage the Pain
You can relieve mild discomfort by using over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Additionally, rinsing your mouth with warm salt water can help soothe any swelling or irritation.
2. Swelling or Redness in The Gums
As your wisdom teeth begin to erupt, you may notice swelling or redness in the gums at the back of your mouth. This is a natural response of the body to the pressure being exerted by the teeth as they push through the gum tissue.
What Does Swelling Indicate?
Swelling is an indication that your gums are inflamed. If the swelling persists or worsens, it could be a sign that the gums are becoming infected, which may require immediate dental attention.
Managing Swelling
To reduce swelling, apply a cold compress to the outside of your cheek in the affected area. Avoid hot or spicy foods that can irritate the swollen gums. Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, such as ibuprofen, can also help reduce both pain and swelling.
3. Bleeding or Gums That Are Tender to The Touch
When wisdom teeth come in, they may cause the gums to bleed or become more sensitive. This is because the teeth push through the gums, which can cause minor cuts or tears in the gum tissue.
What Should You Do?
Mild bleeding is usually nothing to worry about and will subside within a few days. However, if the bleeding persists or is excessive, it’s important to contact your dentist as it could indicate a more serious issue, such as an infection.
Brushing your teeth gently in the affected area and using a soft-bristled toothbrush can help prevent further irritation and keep your gums clean.
4. Bad Breath or Unpleasant Taste in the Mouth
If your wisdom teeth are partially erupted, food particles and bacteria can get trapped around the emerging tooth. This can lead to bad breath, also known as halitosis, or a persistent bad taste in the mouth.
Why Does This Happen?
As the wisdom teeth emerge, the gum tissue may form a flap that covers part of the tooth. This can trap food debris, which, when combined with bacteria, creates an environment where bacteria thrive.
This can lead to a foul smell or taste in your mouth.
Managing Bad Breath
Maintaining a proper oral hygiene routine is crucial to managing bad breath. Brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing regularly, and using mouthwash can help eliminate the bacteria that contribute to bad breath.
5. Difficulty Opening Your Mouth Fully
When your wisdom teeth come in, you may experience difficulty fully opening your mouth. This can happen due to the pressure exerted by the teeth on the surrounding tissues. The muscle soreness and swelling in the gums can make it uncomfortable to open your mouth wide.
Why Does This Occur?
The jaw muscles may become stiff or inflamed as the teeth emerge. Additionally, the pressure from the teeth can push against the jawbone and surrounding tissues, leading to discomfort when moving the jaw.
Managing Limited Jaw Mobility
Using warm compresses on your jaw can help relax the muscles and reduce discomfort. Gentle jaw exercises can also assist in restoring normal movement. If this issue persists, consult with your dentist.
6. Headaches
In some cases, emerging wisdom teeth can lead to tension or pressure in the jaw, which can result in headaches. These headaches may feel like tension headaches, particularly in the area around your temples and the back of your head.
Why Do Wisdom Teeth Cause Headaches?
The pressure caused by wisdom teeth pushing through the gums can affect the muscles and nerves in the jaw, leading to referred pain in the head. Additionally, any swelling or inflammation caused by the teeth can contribute to headache symptoms.
Managing Headaches
If you experience headaches due to your wisdom teeth, over-the-counter pain relievers may provide relief. If the headaches persist, consult with your dentist or healthcare provider to rule out any underlying dental or health issues.
7. Infection or Gum Abscess
Sometimes, wisdom teeth can become infected, especially if they only partially emerge or if they are impacted. A gum abscess may form around the affected tooth, which can lead to severe pain, swelling, and even fever.
What Are the Symptoms of an Infection?
Increased pain or tenderness around the wisdom tooth
Pus or fluid draining from the swollen area
Red, swollen, and tender gums
Fever or a general feeling of illness
What Should You Do If You Suspect an Infection?
If you suspect an infection, it is crucial to seek prompt dental care.
Infections can lead to more serious complications if left untreated.
Your dentist may recommend antibiotics or, in some cases, the removal of the affected wisdom tooth.
8. Crowding or Shifting of Other Teeth
As your wisdom teeth come in, they can push against the other teeth in your mouth. This can cause shifting or crowding, which may result in discomfort or changes in your bite.
Why Does This Happen?
The emerging wisdom teeth can exert pressure on the adjacent teeth, causing them to move out of alignment. This is particularly common in individuals who do not have enough space in their mouths for the wisdom teeth to emerge properly.
What to Do About Shifting Teeth
If your teeth begin to shift or feel crowded, it may be necessary to have your wisdom teeth evaluated by a dentist or orthodontist. In some cases, extraction of the wisdom teeth may be recommended to prevent further dental issues.
9. Changes in Your Bite
If your wisdom teeth are coming in at an angle or are impacted, they may not emerge properly, which can affect your bite.
An improper bite can lead to pain or discomfort while chewing.
How Do Impacted Wisdom Teeth Affect Your Bite?
Impacted wisdom teeth can press against the surrounding teeth, misaligning your bite. This can make it difficult to chew food properly and may even cause jaw pain.
When to Seek Dental Advice
If you notice changes in your bite or difficulty chewing, it is important to schedule an appointment with your dentist. They can evaluate the alignment of your teeth and determine whether any intervention is necessary.
10. Cyst Formation Around the Tooth
In some cases, cysts can develop around the wisdom teeth as they erupt. These cysts are usually fluid-filled sacs that can cause pain, swelling, and damage to surrounding tissues, including the jawbone and teeth.
What Are the Signs of a Cyst?
Increased swelling or tenderness around the wisdom tooth
Pain that persists or worsens
A noticeable lump or bump in the gums
What Should You Do?
If you suspect the formation of a cyst, seek immediate dental care. Your dentist may recommend removing the cyst and the affected wisdom tooth to prevent further complications.
Conclusion
Wisdom teeth are a natural part of the aging process, but they can cause discomfort and complications as they emerge. If you experience pain, swelling, or other signs that your wisdom teeth are coming in, it’s important to manage the symptoms and consult with your dentist if necessary. Early intervention can help prevent more serious issues such as infections, cysts, and misalignment.