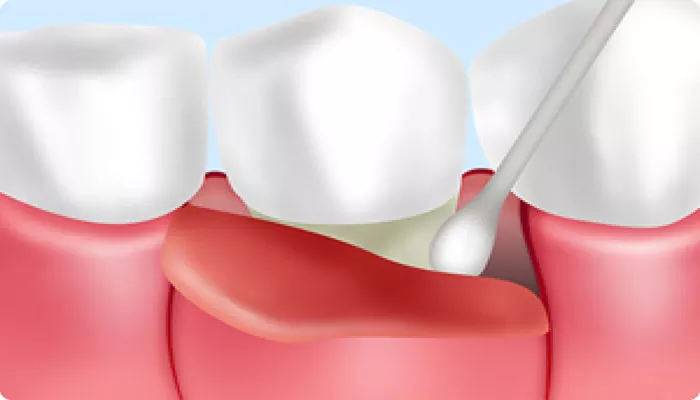
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common dental issue that can affect individuals of all ages. One of the most concerning symptoms of gum disease is the formation of deep gum pockets, which occur when the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, creating spaces where bacteria can accumulate. These deep pockets, also called periodontal pockets, are not only unsightly but can also lead to serious complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the healing potential of deep gum pockets, how they develop, and the available treatments to manage and prevent further damage.
What Are Deep Gum Pockets?
Gum pockets are the spaces or gaps that form between the teeth and the gums. Healthy gums typically fit snugly around the teeth, creating a shallow pocket of around 1 to 3 millimeters in depth. However, when plaque and tartar buildup is not removed, bacteria begin to infect the gums, leading to inflammation and the development of deeper pockets. These pockets can range in depth from 4 millimeters to 10 millimeters or more, with the deeper pockets being more difficult to treat.
As gum disease progresses, the inflammation can cause the gum tissue to recede, pulling away from the teeth. The deeper the pocket, the greater the risk of bacterial growth, which can contribute to tooth loss and other serious oral health issues.
Deep gum pockets are a clear sign of advanced gum disease, often referred to as periodontitis.
Can Deep Gum Pockets Heal on Their Own?
The healing potential of deep gum pockets largely depends on the severity of the condition. In the early stages of gum disease, also known as gingivitis, the gums may bleed and swell, but they do not typically form deep pockets. At this stage, the gum tissue can usually heal with improved oral hygiene practices such as regular brushing and flossing, and professional cleanings by a dentist or hygienist.
However, once deep gum pockets have formed, they do not heal on their own without intervention. In fact, they can worsen over time, leading to more significant damage to the gum tissue and the underlying bone structure. The good news is that with proper treatment and care, deep gum pockets can be managed and, in some cases, reduced.
Treatment Options for Deep Gum Pockets
Professional Cleaning
The first step in treating deep gum pockets is to thoroughly remove the plaque and tartar buildup that is contributing to the infection. A dentist or dental hygienist will perform a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing. This process involves:
Scaling: The removal of plaque and tartar from both above and below the gum line.
Root Planing: Smoothing the surfaces of the tooth roots to remove any rough spots where bacteria can cling.
Scaling and root planing can help reduce the depth of gum pockets and promote healing of the gum tissue. This treatment is typically effective in the early stages of periodontitis and can prevent further progression of gum disease.
Surgical Procedures
If deep gum pockets persist or do not respond to non-surgical treatments, surgical procedures may be necessary to repair the damage. Some common surgical options include:
Flap Surgery: The gums are lifted back to allow the dentist to clean the roots more thoroughly. The gums are then repositioned and sutured back into place.
Bone Grafting: In cases where the bone has been severely damaged, bone grafting may be used to promote new bone growth and support the teeth.
Soft Tissue Grafts: If gum recession has occurred, a soft tissue graft may be performed to restore lost gum tissue.
These procedures are typically recommended when deep gum pockets have resulted in significant damage to the gum tissue or bone structure. While surgical interventions are more invasive, they can help prevent further damage and improve the chances of healing.
Ongoing Care and Maintenance
Even after treatment for deep gum pockets, ongoing care is essential to maintain gum health and prevent the recurrence of the condition.
This includes:
Good Oral Hygiene: Brushing at least twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce plaque buildup.
Regular Dental Check-ups: Regular visits to the dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups will help monitor the health of your gums and ensure that any issues are addressed early.
Lifestyle Changes: Avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy diet can significantly improve the health of your gums and help prevent further complications.
The Role of Gum Pocket Depth in Treatment
The depth of the gum pockets plays a crucial role in determining the appropriate treatment. Shallow pockets (1 to 3 millimeters) typically do not require extensive treatment, as they can be managed with improved oral hygiene and professional cleanings. However, pockets deeper than 4 millimeters are more concerning and may require scaling and root planing or even surgical interventions.
In general, the deeper the pocket, the more difficult it is to treat, and the greater the risk of tooth loss or other complications. It is important to address deep gum pockets as soon as possible to prevent further damage and maintain optimal oral health.
Preventing Deep Gum Pockets
Prevention is always the best approach when it comes to gum disease. By practicing good oral hygiene habits and maintaining regular dental visits, you can reduce the risk of developing deep gum pockets. Here are some preventive measures:
Brush Properly: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to brush your teeth at least twice a day. Pay close attention to the gum line, where plaque tends to accumulate.
Floss Daily: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and along the gum line, areas that a toothbrush cannot reach.
Visit the Dentist Regularly: Regular dental check-ups allow your dentist to monitor your gum health and catch any early signs of gum disease before they become more severe.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease and can contribute to the development of deep gum pockets. Quitting smoking can significantly improve your gum health.
Conclusion
Deep gum pockets are a serious sign of periodontal disease, but with early intervention and appropriate treatment, they can be managed and even reduced. While deep gum pockets do not heal on their own, various treatment options, including professional cleanings, scaling and root planing, and surgical procedures, can help restore gum health. Preventing gum disease in the first place through proper oral hygiene and regular dental visits is the best way to protect your gums and maintain a healthy smile.