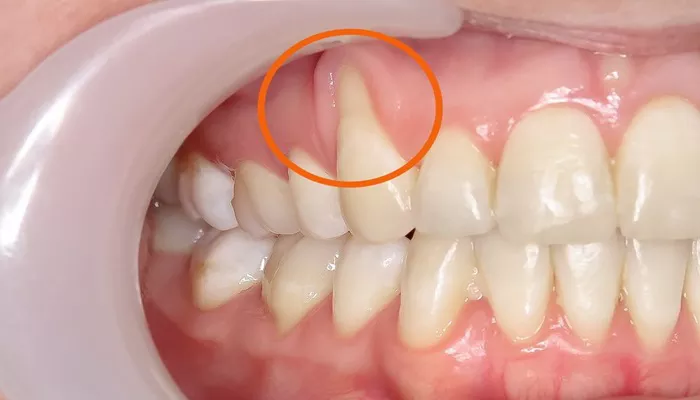
Gum recession is a common dental issue that many people experience over time. It occurs when the gum tissue around the teeth pulls back or wears away, exposing more of the tooth or even the tooth’s root. This condition can lead to a variety of problems, including increased sensitivity, higher risk of cavities, and potential tooth loss. Many people wonder whether gum recession is reversible. In this article, we will explore the causes of gum recession, how it affects oral health, and whether or not it can be reversed.
What Is Gum Recession?
Gum recession is the process where the gum tissue that surrounds your teeth starts to pull away or shrink, exposing the root surface. This exposes the vulnerable root surface, which is not protected by enamel, the hard outer layer of the tooth. As the gums recede, the exposed root can become more sensitive to hot, cold, or even sweet foods. In severe cases, it can lead to tooth decay and loss if not addressed properly.
Causes of Gum Recession
There are several factors that can contribute to gum recession. The most common causes include:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that can cause gum disease, which can lead to gum recession if left untreated.
Gum Disease: Gingivitis and periodontitis are forms of gum disease that can cause the gums to become inflamed and infected. Over time, this inflammation can lead to the loss of gum tissue and the recession of the gums.
Genetics: Some people are more prone to gum recession due to their genetic makeup. If your parents or grandparents had gum recession, you may be more likely to develop it.
Aggressive Brushing: Brushing your teeth too hard or using a toothbrush with hard bristles can cause damage to the gum tissue, leading to recession.
Tobacco Use: Smoking or chewing tobacco can contribute to gum recession by decreasing blood flow to the gums and increasing the risk of gum disease.
Teeth Grinding: Grinding your teeth or clenching your jaw can put excess pressure on your gums, causing them to recede over time.
Hormonal Changes: Changes in hormone levels, such as during pregnancy or menopause, can make the gums more vulnerable to recession.
Misaligned Teeth or Crooked Bite: If your teeth are not properly aligned, certain teeth may experience more pressure, leading to gum recession.
How Does Gum Recession Affect Your Oral Health?
Gum recession can have several negative effects on your oral health.
These include:
Increased Sensitivity
As the gum tissue recedes, the tooth’s root becomes exposed. This root is not protected by enamel, making it more sensitive to temperature changes, acidic foods, and even brushing. Many people with gum recession report discomfort or pain when eating or drinking cold or hot substances.
Higher Risk of Cavities
The roots of the teeth are softer than the enamel, making them more susceptible to cavities and decay. If gum recession exposes the roots, they become more vulnerable to bacterial invasion. This increases the risk of tooth decay and requires more diligent oral care to prevent further damage.
Tooth Loss
If gum recession is left untreated, the supporting bone structure may weaken, which can eventually lead to tooth mobility or even tooth loss. The gum tissue helps to anchor the teeth in place, and when the gums recede significantly, the foundation for your teeth can become unstable.
Aesthetic Concerns
Gum recession can also affect the appearance of your smile. When the gum tissue recedes, it may cause your teeth to appear longer than normal, which can be a cosmetic concern for many people.
Can Gum Receding Be Reversed?
The question of whether gum recession is reversible depends on the extent of the recession and the underlying causes. In general, once gum tissue has receded, it does not regenerate naturally. However, in some cases, gum recession can be treated and improved with proper care and medical intervention.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Gum Recession
In the early stages of gum recession, when the recession is minimal, it may be possible to manage and improve the condition with non-surgical treatments. These treatments can help reduce the recession and prevent it from worsening.
1. Improved Oral Hygiene
The first step in treating gum recession is improving oral hygiene. Brushing your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and using floss or interdental brushes can help remove plaque and bacteria that contribute to gum disease. This can prevent further gum recession and help maintain the health of the gums.
2. Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure performed by a dentist or dental hygienist. During this procedure, the dentist removes plaque and tartar buildup from both the surface of the teeth and the root area. This treatment helps reduce gum inflammation and allows the gums to heal and reattach to the teeth.
3. Desensitizing Treatments
If gum recession has caused increased sensitivity, your dentist may recommend desensitizing treatments. These treatments involve applying special gels or varnishes to the exposed root surface, which can help reduce sensitivity and discomfort.
4. Correcting Brushing Technique
If your gum recession is caused by aggressive brushing, your dentist may recommend switching to a soft-bristled toothbrush and adjusting your brushing technique. Brushing with excessive force or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can cause further damage to the gums.
Surgical Treatment for Gum Recession
In cases of advanced gum recession where the gum tissue has significantly receded, surgical intervention may be necessary to restore the gums and prevent further damage. Surgical procedures for gum recession include:
1. Gum Graft Surgery
Gum graft surgery involves taking tissue from another part of the mouth, such as the roof of the mouth, and grafting it onto the affected area of the gums. This procedure helps restore the gum tissue, covering the exposed tooth roots and preventing further recession.
There are different types of gum grafts, including:
Connective Tissue Grafts: This is the most common type of gum graft, where tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth and stitched onto the receded area.
Free Gingival Grafts: In this type, tissue is directly taken from the roof of the mouth and placed on the receded area.
Pedicle Grafts: This involves using tissue from the gum near the affected area to cover the exposed root.
2. Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST)
The Pinhole Surgical Technique is a minimally invasive procedure that involves making small holes in the gum tissue and using special instruments to gently reposition the gums over the exposed roots. This technique does not require incisions or sutures and has a quicker recovery time compared to traditional gum graft surgery.
3. Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR)
Guided Tissue Regeneration is a surgical technique that involves using a special membrane to encourage the growth of new gum tissue around the exposed tooth roots. This technique is often used when there is significant bone loss due to gum recession.
How to Prevent Gum Recession
Preventing gum recession is essential for maintaining healthy gums and teeth. Here are some tips to help prevent gum recession:
Brush Gently: Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle brushing technique to avoid damaging your gums.
Floss Regularly: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles between your teeth and along the gum line.
Avoid Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco increase your risk of gum disease and gum recession.
Wear a Mouthguard: If you grind your teeth at night, consider wearing a mouthguard to protect your teeth and gums.
Visit the Dentist Regularly: Regular dental checkups allow your dentist to detect early signs of gum disease and take preventive measures.
Conclusion
While gum recession is not typically reversible on its own, it is treatable and manageable. With proper care, gum recession can be prevented from worsening, and in some cases, surgical procedures can help restore the gum tissue. It is important to take preventive measures and seek professional dental care if you notice signs of gum recession.