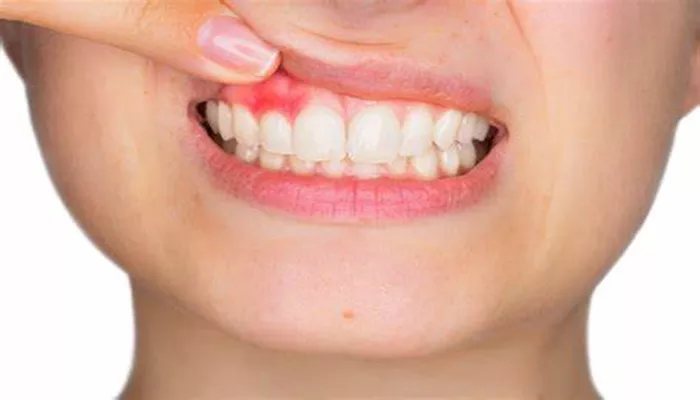
Gum inflammation, also known as gingivitis, is a common and treatable condition that can affect individuals of all ages. It is characterized by swelling, redness, and tenderness of the gums, often accompanied by bleeding, especially when brushing or flossing. Though it may seem like a mild issue at first, if left untreated, gum inflammation can lead to more severe dental problems such as periodontitis, a serious gum disease that can result in tooth loss. Understanding the main cause of gum inflammation and how it develops is essential for maintaining good oral health.
The Primary Cause of Gum Inflammation: Poor Oral Hygiene
The most significant cause of gum inflammation is poor oral hygiene. When proper brushing and flossing techniques are not followed, plaque—a sticky, colorless film of bacteria—builds up on the teeth and gums. If not removed, plaque can harden into tartar, a substance that cannot be removed by brushing alone. Plaque and tartar provide a breeding ground for harmful bacteria, which can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation.
How Plaque Contributes to Gum Inflammation
Plaque forms when food particles and bacteria combine in the mouth. If plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it can start to irritate the gum tissue, leading to symptoms of gingivitis. Initially, the gums may appear red and swollen, and they may bleed slightly when touched or brushed. This early stage of gum disease, called gingivitis, is typically reversible with proper oral care.
When plaque turns into tartar, it further aggravates the gums. Tartar cannot be removed through regular brushing; it requires a professional cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist. As tartar accumulates, it can cause the gums to recede, and pockets may form between the gums and teeth. These pockets trap even more bacteria, making it more challenging to remove plaque and tartar and leading to chronic inflammation and infection.
Other Contributing Factors to Gum Inflammation
While poor oral hygiene is the primary cause of gum inflammation, other factors can contribute to the development of gingivitis and other gum-related issues. Some of these include:
1. Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking or using other tobacco products significantly increases the risk of gum disease. Tobacco use weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off bacterial infections in the gums. Additionally, tobacco products can lead to reduced blood flow to the gums, impairing healing and increasing the likelihood of gum inflammation.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal changes during pregnancy, menstruation, puberty, and menopause can affect the gum tissue. These hormonal fluctuations can increase the gums’ sensitivity to plaque, making them more prone to inflammation. For instance, pregnant women often experience a condition called pregnancy gingivitis, which is characterized by swollen, bleeding gums. The increased levels of estrogen and progesterone during pregnancy can cause the gums to become more sensitive and vulnerable to infection.
3. Medications
Certain medications can contribute to gum inflammation as a side effect. Drugs that reduce saliva flow, such as antihistamines, decongestants, and some medications for high blood pressure or depression, can result in dry mouth, which increases the risk of plaque buildup. Additionally, some medications, such as phenytoin (used to treat seizures) and calcium channel blockers (used to treat heart conditions), can cause gum overgrowth, making it difficult to maintain proper oral hygiene.
4. Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can make the gums more susceptible to inflammation. Conditions such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and certain autoimmune diseases can impair the body’s immune response, increasing the risk of gum disease. People with diabetes, for example, are at higher risk for gum problems because high blood sugar levels can contribute to inflammation in the gums.
5. Poor Nutrition
A diet lacking essential nutrients can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight off infections, including those affecting the gums. A deficiency in vitamin C, for example, can lead to scurvy, a disease that causes swollen, bleeding gums. Ensuring that the body receives adequate nutrition is crucial for maintaining healthy gums.
6. Stress
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and increase the risk of infection, including gum disease. Stress can also lead to behaviors that harm oral health, such as poor oral hygiene, smoking, or teeth grinding. People under stress may also have a higher tendency to neglect their oral health, which can contribute to gum inflammation over time.
7. Genetics
Genetics can also play a role in a person’s susceptibility to gum disease. Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing gingivitis and other gum-related problems, regardless of how well they care for their teeth. While genetics may not be the primary cause, it can certainly increase a person’s risk.
8. Age
As people age, the likelihood of experiencing gum disease increases. Older adults may experience gum recession, which exposes the roots of the teeth and makes them more susceptible to inflammation and infection. Additionally, age-related factors such as medication use, dry mouth, and other health issues can contribute to the development of gum disease.
The Signs and Symptoms of Gum Inflammation
Recognizing the signs of gum inflammation is crucial for early intervention and preventing the progression to more severe gum disease. Some common signs of gingivitis and gum inflammation include:
Red, swollen gums: Healthy gums should be firm and pink.
Inflammation causes the gums to become red and swollen.
Bleeding gums: One of the most common symptoms of gum inflammation is bleeding when brushing or flossing.
Tenderness or pain: Inflamed gums can become sensitive to touch, making brushing and flossing uncomfortable.
Bad breath: Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth can be a sign of gum disease.
Receding gums: As gum inflammation progresses, the gums may begin to recede, making the teeth appear longer.
Loose teeth: In severe cases, gum disease can affect the stability of teeth, causing them to loosen.
How to Prevent And Treat Gum Inflammation
The good news is that gum inflammation is preventable and treatable with proper oral care and lifestyle changes. Here are some steps to prevent and manage gum inflammation:
1. Practice Good Oral Hygiene
The most effective way to prevent gum inflammation is by brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily. This helps remove plaque before it has a chance to harden into tartar. Additionally, using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria in the mouth.
2. Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Routine dental checkups and cleanings are essential for maintaining healthy gums. Your dentist or dental hygienist can remove plaque and tartar buildup that you may not be able to reach with regular brushing and flossing. Professional cleanings every six months are typically recommended for most individuals.
3. Quit Smoking
Quitting smoking or using tobacco products can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease. By quitting, you improve blood flow to your gums and allow them to heal more effectively.
4. Eat a Balanced Diet
Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support a healthy immune system and promote gum health. Avoiding sugary snacks and drinks can prevent plaque buildup and reduce the risk of inflammation.
5. Manage Stress
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or other coping mechanisms can help reduce the impact of stress on your oral health and overall well-being.
6. Seek Professional Treatment
If you notice signs of gum inflammation, it’s essential to seek professional treatment as soon as possible. Your dentist may recommend scaling and root planing (a deep cleaning procedure) or prescribe antibiotics to help clear up an infection.
Conclusion
The main cause of gum inflammation is poor oral hygiene, leading to the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth and gums. However, several other factors, including smoking, hormonal changes, medications, and medical conditions, can also contribute to gum problems. Recognizing the early signs of gum inflammation and taking steps to improve your oral health can help prevent the progression of gum disease.