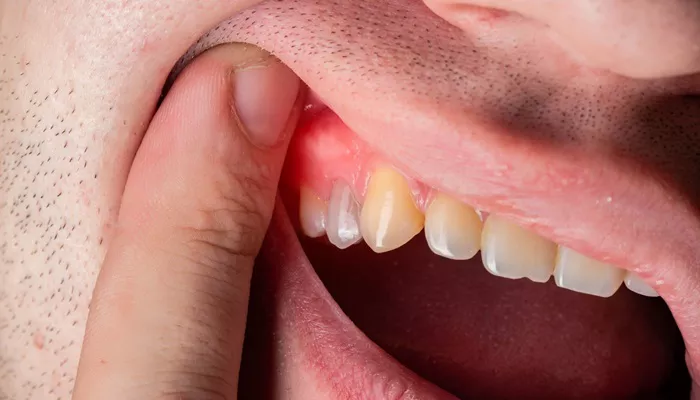
Gum infections are common dental problems that can affect individuals of all ages. These infections, if left untreated, can lead to more severe dental issues, such as gum disease, tooth loss, and even systemic health problems. It’s crucial to identify and address gum infections promptly to prevent further complications.
This guide provides a detailed approach to understanding, diagnosing, and treating gum infections. From initial symptoms to professional treatment options, we cover everything you need to know to take care of your oral health and prevent future infections.
What Is A Gum Infection?
A gum infection, also known as gingivitis or periodontitis depending on its severity, occurs when bacteria invade the soft tissues of the gums. These infections usually start as a result of poor oral hygiene, which leads to the build-up of plaque on the teeth and gums. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation, bleeding, and, if left untreated, more serious oral health problems.
Causes of Gum Infections
Several factors contribute to the development of gum infections:
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing habits allow plaque to build up on the teeth and gums, leading to infection.
Tobacco Use: Smoking and chewing tobacco can damage the gums and reduce the body’s ability to fight infections.
Poor Nutrition: A lack of essential nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can weaken the gums and make them more susceptible to infection.
Health Conditions: Diseases like diabetes and autoimmune disorders can increase the risk of gum infections.
Medications: Some medications can affect the health of your gums, such as those that reduce saliva production or affect the body’s immune response.
Signs And Symptoms of a Gum Infection
Recognizing the symptoms of a gum infection early can help prevent the infection from progressing. Some common signs include:
Red, Swollen Gums: Healthy gums should be firm and pink. Infection causes them to become swollen and red.
Bleeding Gums: Gums may bleed when brushing or flossing, which is a sign of inflammation and infection.
Bad Breath (Halitosis): Persistent bad breath can be a sign of gum infection due to the bacteria present in the mouth.
Pain or Tenderness: Infected gums can be painful to touch and may cause discomfort while chewing.
Receding Gums: Gum infection can cause the gums to recede, which exposes more of the tooth and can lead to tooth sensitivity.
Abscesses: Pus-filled pockets (abscesses) can form around the infected gums, indicating a more severe infection.
How to Treat A Gum Infection at Home
While visiting a dentist is crucial for proper treatment, there are steps you can take at home to manage a mild gum infection and alleviate discomfort.
1. Improve Oral Hygiene
The most effective way to prevent and treat gum infections is by practicing proper oral hygiene:
Brush Twice a Day: Use fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean your teeth and gums. Make sure to brush for at least two minutes, reaching all surfaces of your teeth.
Floss Daily: Flossing removes food particles and plaque that brushing might miss. It’s essential to floss between your teeth to prevent gum disease.
Use Mouthwash: Antiseptic mouthwashes can help reduce bacteria in the mouth, promoting healthier gums and preventing infection.
2. Saltwater Rinse
A saltwater rinse is an effective natural remedy to soothe inflamed gums and help kill bacteria. Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth for 30 seconds, up to three times a day.
3. Apply a Cold Compress
If the infection causes swelling or pain, applying a cold compress to the affected area can reduce inflammation and numb the discomfort. Wrap ice in a cloth and place it against your cheek for 10–15 minutes at a time.
4. Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers
If you experience pain or discomfort, over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate symptoms. Be sure to follow the recommended dosage instructions on the packaging.
Professional Treatment for Gum Infections
If home remedies don’t resolve the issue or if the infection worsens, it’s essential to seek professional dental care. A dentist can provide treatments tailored to the severity of your gum infection.
1. Scaling and Root Planing
For mild to moderate gum infections, a dentist may recommend scaling and root planing. This procedure involves deep cleaning of the teeth, removing plaque and tartar from below the gum line. It helps prevent the infection from spreading deeper into the gums and restores gum health.
2. Antibiotics
If the infection is more severe, a dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help fight the bacteria. Antibiotics can be taken orally or applied directly to the gums in the form of a gel or rinse. This can be especially helpful if there is an abscess or widespread infection.
3. Surgery
In advanced cases of gum disease, surgical procedures may be necessary to restore gum health. These include:
Flap Surgery: The dentist may make small incisions in the gums to access deeper areas, remove infected tissue, and clean the roots of the teeth.
Bone Grafting: If the infection has caused significant damage to the bone supporting the teeth, bone grafts may be used to rebuild the area.
Gum Grafting: In cases of severe gum recession, tissue may be taken from another part of the mouth and grafted onto the affected area to cover exposed tooth roots.
4. Laser Treatment
Laser treatment is an advanced procedure used to treat gum infection. A laser is used to remove infected tissue and bacteria from the gums, promoting faster healing with minimal discomfort and a reduced risk of infection.
Preventing Gum Infections
While treating a gum infection is essential, preventing future infections is equally important. Here are some tips to keep your gums healthy:
Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss daily to remove plaque and prevent gum disease.
Regular Dental Checkups: Visit your dentist at least twice a year for professional cleanings and checkups.
Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, especially vitamin C, to support healthy gums.
Quit Smoking: Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gum disease and other oral health problems. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum infections.
Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your mouth moist and wash away bacteria and food particles.
When to See A Dentist
If your gum infection doesn’t improve with home treatment, or if you experience symptoms such as severe pain, swelling, or abscesses, it’s time to consult a dentist. Early intervention is crucial in preventing more serious complications.
Conclusion
Gum infections, although common, can lead to significant dental and health issues if left untreated. By practicing good oral hygiene and seeking timely professional treatment, you can effectively manage and prevent gum infections. Always consult a dentist if you notice persistent symptoms, as early treatment is key to preserving your oral health and preventing long-term damage.