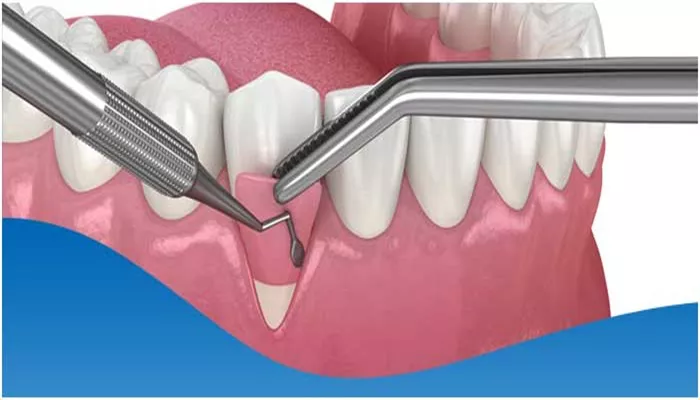
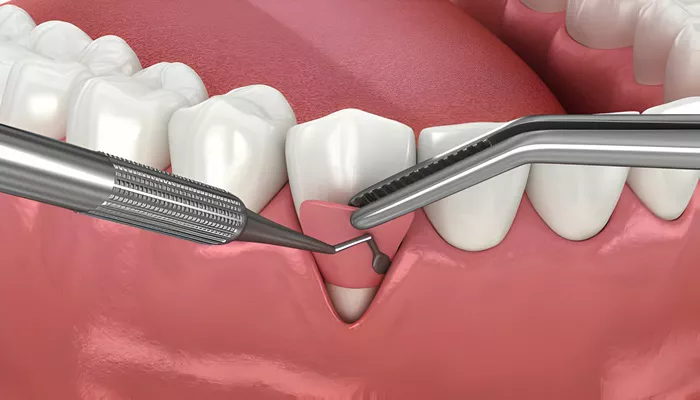
What Is Gum Grafting
Gum grafting, also known as gingival grafting, is a periodontal procedure aimed at restoring or augmenting gum tissue. It is often recommended when gum recession has exposed the tooth roots or compromised gum health.
1. Purpose of Gum Grafting
Protect Tooth Roots: Gum recession can expose the roots of teeth, increasing sensitivity and the risk of decay. Grafting restores gum coverage over the exposed areas.
Prevent Further Recession: By reinforcing the gumline, grafting can halt or slow further recession.
Enhance Aesthetics: Gum grafting can improve the appearance of a smile by creating a more uniform gumline.
2. Causes of Gum Recession
Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing or flossing can lead to gum disease, a leading cause of recession.
Aggressive Brushing: Brushing too hard or using a stiff-bristled toothbrush can wear away gum tissue.
Genetics: Some individuals are predisposed to gum recession due to genetic factors.
Orthodontic Treatment: Movement of teeth during orthodontic treatment can occasionally contribute to gum recession.
3. Types of Gum Grafts
There are three primary types of gum grafts:
Connective Tissue Grafts: The most common type, which involves harvesting tissue from beneath the palate to cover exposed roots.
Free Gingival Grafts: Tissue is taken directly from the roof of the mouth and grafted to the gumline.
Pedicle Grafts: Tissue is moved from a nearby area to cover the recession without separating it completely.
Gum Grafting Procedure
The gum grafting procedure typically involves several steps, each designed to ensure effective and predictable results.
1. Pre-Surgical Assessment
Before the procedure, the periodontist will:
Evaluate the extent of gum recession.
Discuss treatment goals and expectations with the patient.
Take measurements and possibly X-rays to plan the surgery.
2. Anesthesia
The procedure begins with the administration of local anesthesia to numb the treatment area, ensuring patient comfort throughout the surgery.
3. Tissue Harvesting
The surgeon may harvest tissue from the roof of the mouth or another donor site, depending on the type of graft being performed. Alternatively, processed tissue from a donor source may be used.
4. Graft Placement
The harvested tissue is carefully sutured to the recessed gum area.
The surgeon ensures that the graft covers the exposed root adequately and integrates well with the surrounding tissue.
5. Post-Surgical Care
Once the graft is in place, the surgical site is covered with a protective dressing to facilitate healing and minimize discomfort.
Gum Grafting Recovery
The recovery period is a critical phase that ensures the success of the gum graft. Here’s what to expect and how to care for your gums during this time.
1. Healing Time
Initial healing takes about 1–2 weeks, but complete healing and integration of the graft may take several months.
The grafted area may initially appear swollen or discolored, which is normal and resolves over time.
2. Managing Discomfort
Mild pain or discomfort is common, which can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or medications prescribed by the periodontist.
An ice pack applied to the outside of the face can help reduce swelling during the first 24 hours.
3. Dietary Modifications
Stick to soft, non-spicy foods during the initial healing phase to avoid irritating the grafted area.
Avoid hot beverages and hard or crunchy foods that could dislodge the graft.
4. Oral Hygiene
Gently rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash as instructed by your dentist to prevent infection.
Avoid brushing or flossing directly over the graft site until advised.
5. Follow-Up Appointments
Regular follow-up visits allow the periodontist to monitor healing progress and address any complications.
Gum Grafting Before and After
1. Before Gum Grafting
Understanding the transformations achieved through gum grafting can help set realistic expectations.
2. After Gum Grafting
Symptoms: Patients often experience sensitivity, exposed roots, and an uneven gumline.
Concerns: Many seek treatment for aesthetic reasons, such as a “toothy” smile, or functional issues like discomfort during eating.
Improved Aesthetics: The gumline appears more even and healthy, enhancing the overall smile.
Reduced Sensitivity: Covering exposed roots alleviates sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods.
Enhanced Gum Health: The procedure restores gum tissue, providing better protection against decay and further recession.
Gum Grafting Cost
The cost of gum grafting varies depending on several factors, including the complexity of the procedure, the number of teeth involved, and geographic location.
1. Average Cost
The cost typically ranges from $600 to $1,200 per tooth.
If donor tissue is used, costs may be higher due to additional processing and materials.
2. Insurance Coverage
Many dental insurance plans partially cover gum grafting if it is deemed medically necessary.
Cosmetic procedures, however, may not be covered.
3. Additional Costs
Pre-surgical consultations, imaging, and follow-up care may incur additional fees.
Discussing costs and payment plans with your dental office beforehand can help with financial planning.
FAQs about Gum Grafting
1. How long does gum grafting last?
Gum grafting is a durable solution, often lasting a lifetime with proper care. The longevity depends on factors like:
Oral Hygiene: Consistent brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can maintain the graft.
Lifestyle Habits: Avoiding smoking and managing conditions like bruxism (teeth grinding) can prolong the graft’s success.
Underlying Conditions: If the cause of gum recession is treated effectively, the graft is more likely to remain stable.
Regular follow-ups with your dentist are essential to monitor the graft’s health.
2. How painful is gum grafting?
The procedure itself is typically not painful, as dentists use local anesthesia to numb the area. Post-operative discomfort varies but is generally manageable. Here’s what to expect:
Mild to Moderate Discomfort: You may feel soreness or sensitivity for a few days after the procedure.
Pain Management: Dentists usually prescribe pain relievers or recommend over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen.
Soft Diet Required: Eating soft foods can help minimize discomfort during the healing process.
Following your dentist’s aftercare instructions can help ensure a smooth recovery.
3. Do dentists recommend gum grafts?
Yes, dentists recommend gum grafts when gum recession has exposed the roots of teeth, leading to:
Sensitivity: To hot or cold temperatures.
Aesthetic Concerns: Improving the appearance of the gumline.
Protecting Tooth Roots: Preventing further damage or decay.
Supporting Overall Oral Health: Gum grafts stabilize the gum tissue and protect teeth from potential complications.