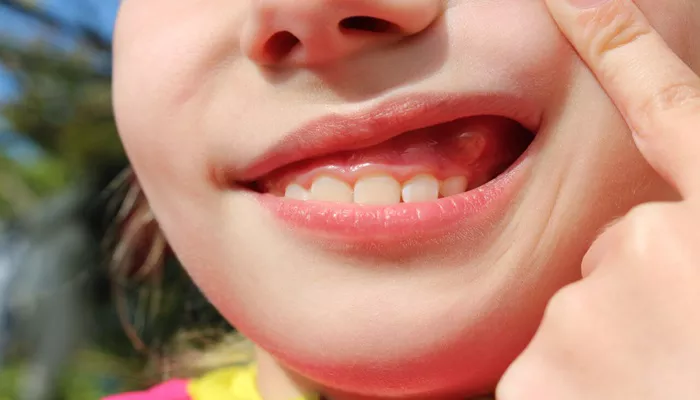
Swollen gums, also known as gingival swelling, are a common dental issue that many individuals experience at some point in their lives. This condition can range from mild discomfort to significant pain and inflammation. Swollen gums can be caused by a variety of factors, from poor oral hygiene to more serious health issues. While the discomfort associated with swollen gums is often temporary, it can sometimes lead to more severe oral health problems, such as gum disease or tooth loss, if left untreated.
This article will provide a comprehensive guide on how to treat swollen gums, highlighting common causes, effective treatment methods, and tips for prevention. Whether you’re dealing with mild swelling or more persistent gum issues, understanding the root cause and appropriate treatment options is crucial to maintaining good oral health.
What Causes Swollen Gums?
Before delving into the treatment options, it’s important to understand what causes swollen gums. Swelling is often a sign of inflammation and can be triggered by several factors. Below are some of the most common causes:
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
The most common cause of swollen gums is poor oral hygiene. When plaque—the sticky film of bacteria—accumulates on the teeth and gums, it can lead to inflammation. Plaque can irritate the gum tissue, causing it to become swollen and bleed, especially when brushing or flossing.
2. Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease caused by the buildup of plaque on the teeth. This condition is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums, particularly when brushing or flossing. Gingivitis is typically reversible with proper oral care, but if left untreated, it can progress to more severe forms of gum disease.
3. Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a more advanced form of gum disease that can develop from untreated gingivitis. It involves inflammation of the tissues surrounding the teeth and can lead to gum recession, tooth mobility, and even tooth loss. Periodontitis requires professional treatment and may not be fully reversible, but it can be managed with proper care.
4. Pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause hormonal changes that affect gum health, leading to swollen gums, a condition known as pregnancy gingivitis. Increased blood flow to the gums and hormonal fluctuations can make the gums more sensitive, causing them to swell or bleed.
5. Medications
Certain medications can lead to swollen gums as a side effect. Drugs like phenytoin (used to treat epilepsy) and calcium channel blockers (used for high blood pressure) can cause gum overgrowth and inflammation.
6. Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential vitamins, especially Vitamin C, can lead to swollen gums. A deficiency in this vitamin can result in scurvy, a condition that causes bleeding gums and poor wound healing.
7. Infections
Bacterial or viral infections can cause swelling in the gums. Conditions such as abscessed teeth or oral herpes can lead to painful, swollen gums that require immediate medical attention.
8. Allergic Reactions
Allergies to certain foods, dental products, or medications can lead to swollen gums. For example, reactions to toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) can cause irritation and inflammation in the mouth.
How to Treat Swollen Gums: Step-by-Step Guide
Now that we have established the causes of swollen gums, let’s explore the various treatment options available. Whether your swollen gums are caused by gingivitis, an infection, or another factor, there are several ways to alleviate the discomfort and prevent further damage.
1. Improving Oral Hygiene
The first and most important step in treating swollen gums is improving oral hygiene. Poor oral hygiene is the most common cause of gingivitis and swollen gums, so ensuring your teeth and gums are clean will help reduce inflammation and prevent further issues.
Brushing
Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid irritating your gums.
Be sure to brush along the gumline, where plaque buildup is most likely to occur. Brushing for at least two minutes helps remove food particles and plaque.
Flossing
Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline. If your gums are swollen and bleed when you floss, don’t stop! Bleeding gums are a sign of inflammation, and continuing to floss will help reduce this over time.
Mouthwash
Using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help reduce plaque buildup and kill bacteria that may be causing the inflammation.
An antibacterial rinse containing chlorhexidine can be particularly effective in treating gingivitis.
2. Saltwater Rinse
A simple and effective home remedy for swollen gums is a saltwater rinse. Saltwater acts as a natural disinfectant and can help reduce inflammation. It also helps to soothe irritated gum tissues.
To make a saltwater rinse, dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water. Swish the solution around your mouth for 30 seconds, making sure it reaches the swollen areas. Repeat this rinse two to three times a day until the swelling subsides.
3. Cold Compress
If your swollen gums are causing pain, applying a cold compress can provide relief. Cold temperatures help constrict blood vessels, reducing swelling and numbing pain.
Wrap some ice cubes in a clean cloth or use a cold pack. Hold it against your face near the swollen area for about 10-15 minutes at a time. Repeat this process every few hours as needed.
4. Topical Treatments
Several over-the-counter topical gels and ointments are available that can help soothe swollen gums. These products often contain benzocaine or other anesthetic ingredients that numb the area and provide temporary relief from pain and discomfort.
Additionally, you can apply a small amount of aloe vera gel or honey to the swollen gums. Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory properties, and honey has antibacterial qualities that can help speed up the healing process.
5. Hydration
Dehydration can exacerbate gum problems, so drinking plenty of water is essential for healthy gums. Staying hydrated helps maintain moisture in the mouth and prevents dry mouth, which can worsen gum irritation and swelling.
6. Visit Your Dentist
If your swollen gums persist despite home treatment or are accompanied by severe pain, pus, or fever, it’s essential to see a dentist. Your dentist will examine your gums and may take X-rays to assess the underlying cause of the swelling.
In cases of gum disease, your dentist may recommend a deep cleaning procedure, such as scaling and root planing, to remove plaque and tartar from below the gumline. If the swelling is caused by an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear up the infection.
7. Addressing Underlying Health Conditions
If your swollen gums are caused by an underlying health issue such as pregnancy, diabetes, or a medication side effect, your healthcare provider will need to address the root cause. For example, adjusting medications or managing blood sugar levels may help reduce gum inflammation.
Prevention of Swollen Gums
The best way to avoid swollen gums is to practice good oral hygiene and maintain regular dental checkups. Here are some additional tips for preventing swollen gums:
Quit smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease and can impair gum healing.
Eat a balanced diet: Ensure you’re getting enough vitamins and minerals, especially Vitamin C, to keep your gums healthy.
Avoid sugary foods and drinks: These can promote plaque buildup, leading to gum irritation and disease.
Visit your dentist regularly: Professional cleanings and exams can help detect and treat gum issues early, before they become more serious.
Conclusion
Swollen gums are a common yet treatable issue that many people face. The key to managing and treating swollen gums lies in identifying the underlying cause and taking appropriate action. Improving oral hygiene, using home remedies like saltwater rinses, and seeking professional dental care when necessary can help reduce swelling and prevent further complications. Remember, if you experience persistent swelling or pain, it’s important to consult with a dentist to ensure that any serious dental conditions are addressed promptly.
Related topics:
- The 8 Best Ways to Stop Gum Recession
- Which Vitamin Deficiency Causes Gum Bleeding?
- How Do I Stop My Gums from Bleeding?