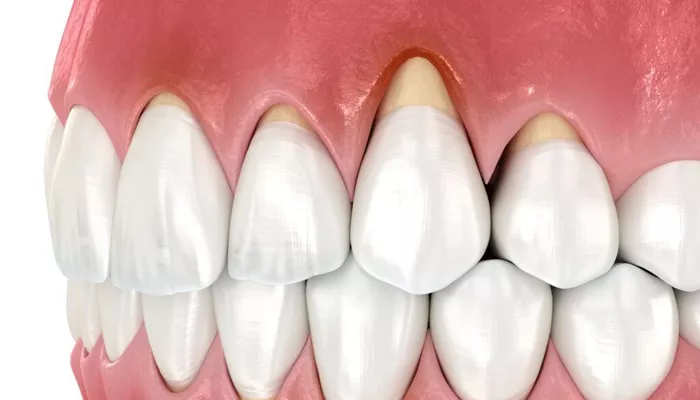
Gum recession is a common dental problem that affects many people, regardless of age. It occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back or wears away, exposing the tooth roots and leading to potential sensitivity, decay, or even tooth loss. This condition often develops gradually, making it difficult to detect in its early stages. Understanding the best ways to stop gum recession is vital for maintaining healthy gums and preventing further complications.
Receding gums are often linked to poor oral hygiene, aggressive brushing, gum disease, or genetic factors. Regardless of the cause, addressing the problem early can help preserve your oral health and restore your smile. In this article, we will explore eight effective ways to stop gum recession and promote healthier gums.
1. Practice Proper Oral Hygiene
Good oral hygiene is the foundation of healthy gums. Regular brushing and flossing can remove plaque and bacteria that contribute to gum recession. Here are some tips for maintaining proper oral hygiene:
Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid damaging your gums.
Brush gently for at least two minutes, twice a day.
Use fluoride toothpaste to strengthen your teeth and prevent decay.
Floss daily to remove debris and plaque between your teeth.
Rinse with an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce harmful bacteria.
Avoid overbrushing or scrubbing too hard, as this can irritate your gums and exacerbate recession.
2. Switch to A Desensitizing Toothpaste
If gum recession has already caused tooth sensitivity, using a desensitizing toothpaste can help. These toothpastes are specially formulated to block the pathways that lead to nerve sensitivity. They also contain fluoride, which helps to strengthen exposed roots and protect against further enamel erosion.
Desensitizing toothpaste can provide relief from discomfort and encourage better oral care practices, making it easier to maintain consistent hygiene habits.
3. Address Underlying Gum Disease
Gum disease, or periodontal disease, is a major cause of gum recession. If you suspect you have gum disease, seek professional treatment promptly. Common treatments include:
Scaling and root planing: A deep cleaning procedure that removes plaque and tartar buildup below the gumline.
Antibiotics: Medications to control bacterial infection and reduce inflammation.
Laser therapy: A minimally invasive option to target diseased tissue and bacteria.
Early intervention can prevent further gum recession and protect your overall oral health.
4. Use a Custom Mouthguard
Teeth grinding, or bruxism, can worsen gum recession by putting excessive pressure on your gums. If you grind your teeth, especially during sleep, consider using a custom mouthguard. These devices cushion your teeth, reduce grinding, and alleviate stress on your gums.
Consult your dentist to have a mouthguard made specifically for your bite. Over-the-counter options may not fit as well and could be less effective.
5. Improve Your Diet
A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can support gum health and prevent further recession. Focus on consuming:
Vitamin C: Found in citrus fruits, berries, and leafy greens, vitamin C helps strengthen gums and combat inflammation.
Calcium: Dairy products, almonds, and leafy greens provide calcium, which supports strong teeth and bones.
Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, these fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties.
Avoid sugary snacks and drinks, as they contribute to plaque buildup and increase the risk of gum disease.
6. Quit Smoking
Smoking is a significant risk factor for gum recession. It weakens your immune system, making it harder for your gums to fight off infections. Smoking also reduces blood flow to the gums, hindering their ability to heal.
Quitting smoking can improve your gum health and reduce the risk of further recession. If you need assistance, consider nicotine replacement therapy, counseling, or support groups to help you break the habit.
7. Consider Gum Grafting Surgery
For severe cases of gum recession, gum grafting surgery may be necessary. This procedure involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth (or using donor tissue) and attaching it to the affected area. Gum grafting can:
Cover exposed roots.
Reduce sensitivity.
Prevent further recession.
Improve the appearance of your gums.
Discuss this option with your dentist or periodontist to determine if it’s the right solution for your condition.
8. Schedule Regular Dental Checkups
Routine dental visits are crucial for monitoring your gum health and addressing potential issues early. During checkups, your dentist can:
Identify signs of gum disease or recession.
Perform professional cleanings to remove plaque and tartar.
Provide personalized recommendations for maintaining healthy gums.
Aim to visit your dentist at least twice a year, or more frequently if you have a history of gum disease or other dental problems.
Conclution
Gum recession is a manageable condition with the right approach. By practicing good oral hygiene, addressing underlying causes, and seeking professional care, you can stop gum recession and protect your oral health. Each of these eight strategies plays a critical role in preventing further damage and promoting healthier gums.
Related topics:
- What Causes Hyperplasia of The Gums?
- Which Vitamin Deficiency Causes Gum Bleeding?
- How Do I Stop My Gums from Bleeding?