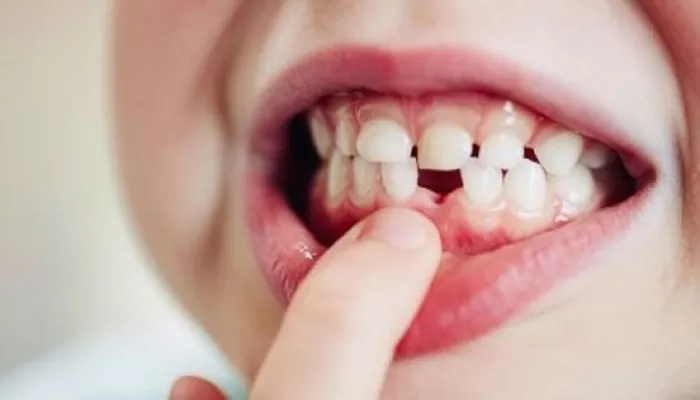
Bleeding gums can be an alarming and uncomfortable experience, often signaling underlying oral health issues. While occasional bleeding might occur due to aggressive brushing or flossing, persistent bleeding is usually a sign of gum inflammation or other conditions. Understanding the causes and taking the right steps can help you manage and prevent bleeding gums effectively.
In this article, we’ll explore the common causes of bleeding gums, actionable remedies, and preventive measures to maintain healthy gums.
Causes of Bleeding Gums
1. Poor Oral Hygiene
Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to the buildup of plaque along the gumline. Over time, this plaque hardens into tartar, irritating the gums and causing them to bleed.
2. Gingivitis
Gingivitis, the earliest stage of gum disease, is a leading cause of bleeding gums. It is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums due to plaque-induced inflammation.
3. Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a severe form of gum disease. This condition damages the soft tissues and bones supporting the teeth, causing more pronounced gum bleeding.
4. Improper Brushing or Flossing Techniques
Using a toothbrush with hard bristles or brushing too aggressively can irritate and damage gum tissue. Similarly, flossing incorrectly can cause small cuts that lead to bleeding.
5. Vitamin Deficiencies
Deficiencies in vitamins, particularly Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) and Vitamin K, can weaken gum tissues and impair the blood’s ability to clot, leading to bleeding gums.
6. Medications
Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can increase the likelihood of gum bleeding. Informing your dentist about your medications can help tailor oral care practices.
7. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and prone to bleeding.
Remedies to Stop Gum Bleeding
1. Improve Oral Hygiene
Brush your teeth twice daily using a soft-bristled toothbrush.
Use fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel and protect gums.
Floss daily to remove plaque and debris between teeth.
Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce bacteria.
2. Use a Saltwater Rinse
Saltwater rinses can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria. Mix half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and swish it around your mouth for 30 seconds twice daily.
3. Adopt Proper Brushing Techniques
Use gentle, circular motions while brushing to avoid damaging gum tissue.
Avoid over-brushing or using excessive force.
Replace your toothbrush every 3-4 months or when the bristles fray.
4. Apply a Cold Compress
If bleeding is accompanied by swelling, apply a cold compress to the affected area. This can reduce inflammation and minimize bleeding.
5. Increase Vitamin Intake
Vitamin C: Found in oranges, strawberries, and broccoli, this vitamin strengthens gum tissue and boosts immunity.
Vitamin K: Found in leafy greens like spinach and kale, this vitamin promotes proper blood clotting.
Consider taking supplements if dietary intake is insufficient, but consult a healthcare provider first.
6. Quit Smoking
Smoking weakens the immune system and impairs the body’s ability to heal, exacerbating gum problems. Quitting smoking can significantly improve gum health.
7. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps flush food particles and bacteria from the mouth, reducing the risk of plaque accumulation.
8. Use Specialized Oral Care Products
Switch to toothpaste and mouthwash formulated for gum health. Products with active ingredients like stannous fluoride, triclosan, or hydrogen peroxide can help reduce inflammation and promote healing.
When to See A Dentist
While home remedies can be effective for minor gum bleeding, persistent or severe cases may indicate serious oral health problems. Schedule a dental appointment if:
Bleeding persists despite improved oral hygiene.
Your gums are swollen, red, or receding.
You experience tooth sensitivity or loose teeth.
You notice pus or a bad taste in your mouth.
You have a history of gum disease or underlying medical conditions.
A dentist will perform a thorough examination, including X-rays if necessary, and recommend treatments such as professional cleaning, scaling, or root planing.
Preventive Measures
1. Maintain Regular Dental Checkups
Visiting the dentist every six months for cleanings and checkups is essential. Professional cleanings remove tartar and prevent gum disease.
2. Adopt a Balanced Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports overall oral health. Limit sugary and acidic foods that promote plaque buildup.
3. Manage Stress
High stress levels can compromise your immune system, making you more susceptible to gum infections. Practice stress-relieving activities like yoga, meditation, or regular exercise.
4. Avoid Teeth Grinding
Grinding your teeth (bruxism) can irritate gums and lead to bleeding. Consider wearing a nightguard if you grind your teeth while sleeping.
5. Replace Worn Dental Appliances
Ill-fitting dentures or orthodontic appliances can irritate gums. Regular adjustments by your dentist can prevent irritation and bleeding.
Conclusion
Bleeding gums are not just a minor annoyance; they can be an indicator of more serious oral health issues. By identifying the cause and taking appropriate measures, you can stop gum bleeding and improve your overall oral hygiene. Combining proper brushing techniques, a balanced diet, and regular dental visits will ensure long-term gum health and a confident smile.
Related topics: